
Esta página no está disponible en español
¿Le gustaría continuar en la página de inicio de Brennan Center en español?
al Brennan Center en inglés
al Brennan Center en español
Subscribe to Our Newsletter Close Stay up to dateEsta página no está disponible en español
¿Le gustaría continuar en la página de inicio de Brennan Center en español?
al Brennan Center en inglés
al Brennan Center en español
Principles for Social Media Use by Law Enforcement
Unfettered social media surveillance by police imperils constitutional rights and marginalized communities. Our best practices help mitigate these risks.
Published: February 7, 2024
Social media is a powerful tool for connection and civic involvement, serving myriad purposes. It facilitates community-building, connecting like-minded people and fostering alliance development, including on sensitive or controversial topics; it helps grassroots movements find financial and other support; it promotes political education; it assists civic organizations in organizing and magnifying the reach of offline efforts; it elevates nonmainstream narratives; it encourages artistic expression; and more. footnote1_bOvTzu2KDUn8 1 See, e.g., Marcia Mundt, Karen Ross, and Charla M. Burnett, “Scaling Social Movements Through Social Media: The Case of Black Lives Matter,” Social Media + Society 4, no. 4 (October–December 2018): 1–14, https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/epub/10.1177/2056305118807911; Jane Hu, “The Second Act of Social-Media Activism,” New Yorker, August 3, 2020, https://www.newyorker.com/culture/cultural-comment/the-second-act-of-social-media-activism; and Shira Ovide, “How Social Media Has Changed Civil Rights Protests,” New York Times, updated December 17, 2020, https://www.nytimes.com/2020/06/18/technology/social-media-protests.html.
Users of color benefit especially from social media’s wide-ranging applications. Black and Hispanic users of X (formerly Twitter) have leveraged that platform to spur political engagement and give voice to underrepresented groups. footnote2_jJxWrLTIyPSH 2 Black Twitter and Hispanic Twitter (like Asian American Twitter and Feminist Twitter) are monikers coined for the space on Twitter (now X) in which people “discuss issues of concern to themselves and their communities — issues they say either are not covered by mainstream media, or are not covered with the appropriate cultural context.” Deen Freelon et al., How Black Twitter and Other Social Media Communities Interact with Mainstream News, Knight Foundation, February 27, 2018, 38–39, https://knightfoundation.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/02/Marginalized-Twitter-v5.pdf. See also Brooke Auxier, “Social Media Continue to Be Important Political Outlets for Black Americans,” Pew Research Center, December 11, 2020, https://www.pewresearch.org/short-reads/. 2020/12/11/social-media-continue-to-be-important-political-outlets-for-black-americans. College students of color have used social media to share stories about inequitable or traumatic treatment at predominantly white colleges and universities. footnote3_uVMgzYNsrA7f 3 Christian Peña, “How Social Media Is Helping Students of Color Speak Out About Racism on Campus,” PBS NewsHour, September 8, 2020, https://www.pbs.org/newshour/education/how-social-media-is-helping-students-of-color-speak-out-about-racism-on-campus; and Dominique Skye McDaniel, “As Digital Activists, Teens of Color Turn to Social Media to Fight for a More Just World,” Conversation, April 20, 2023, https://theconversation.com/as-digital-activists-teens-of-color-turn-to-social-media-to-fight-for-a-more-just-world-201841. And “Black Twitter” in particular has a record of pushing the national media to cover overlooked stories. footnote4_c494O50H5jMW 4 Freelon et al., How Black Twitter and Other Social Media Communities Interact, 46–47. See also Auxier, “Social Media Continue to Be Important Political Outlets”; Brooke Auxier, “Activism on Social Media Varies by Race and Ethnicity, Age, Political Party,” Pew Research Center, July 13, 2020, https://www.pewresearch.org/short-reads/2020/07/13/activism-on-social-media-varies-by-race-and-ethnicity-age-political-party; and University of Kansas, “Social Media Use Increases Latino Political Participation,” news release, November 5, 2018, https://news.ku.edu/2018/11/02/social-media-use-increases-latino-political-participation. Research shows that young people of color are the demographic group most likely to turn to social media both to consume news and to amplify their own political involvement. footnote5_hsQJhUkreQ6c 5 Matthew D. Luttig and Cathy J. Cohen, “How Social Media Helps Young People — Especially Minorities and the Poor — Get Politically Engaged,” Washington Post, September 9, 2016, https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/monkey-cage/wp/2016/09/09/how-social-media-helps-young-people-especially-minorities-and-the-poor-get-politically-engaged; Auxier, “Social Media Continue to Be Important Political Outlets”; and Auxier, “Activism on Social Media Varies by Race and Ethnicity, Age, Political Party.” As the Supreme Court has recognized, online platforms “can provide perhaps the most powerful mechanisms available to a private citizen to make his or her voice heard.” footnote6_rnhomjQkacr9 6 Packingham v. North Carolina, 582 U.S. 98, 107 (2017).
This far-reaching use makes social media an attractive source of information and intelligence for law enforcement. Officers can easily view publicly available information online and follow individuals and hashtags, often without even needing an account. They can also create undercover accounts to join online groups, monitor activity anonymously, or connect directly with individuals — with the attendant risks described below. Social media can provide evidence of criminal activity, from white-collar crime to inciting violence to drug and firearm offenses. It can also be used to commit crimes, such as stalking, harassment, and child sexual exploitation. footnote7_aEPlugikRrif 7 See LexisNexis Risk Solutions, Social Media Use in Law Enforcement: Crime Prevention and Investigative Activities Continue to Drive Usage, November 2014, https://centerforimprovinginvestigations.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/2014-social-media-use-in-law-enforcement-pdf.pdf (documenting multiple use cases of police use of social media).
Many law enforcement agencies contract with software vendors that offer proprietary, opaque computer algorithms to collect and analyze massive amounts of data. These algorithms supply agencies with running reports of social media posts on topics, groups, and individuals of interest, allowing law enforcement to analyze associations, and even discern viewpoints. Such tools facilitate the monitoring, collection, and analysis of data far more quickly and cheaply than any individual officer could accomplish, implicating the Supreme Court’s recognition that a “central aim” of the Constitution’s drafters was “to place obstacles in the way of a too permeating police surveillance.” footnote8_w7xx3j57z0qB 8 Carpenter v. U.S., 138 S. Ct. 2206, 2214 (2018) (quoting U.S. v. Di Re, 332 U.S. 581, 595 (1948)) (internal quotation marks omitted). See also Rachel Levinson-Waldman, “Government Access to and Manipulation of Social Media: Legal and Policy Challenges,” Howard Law Journal 61, no. 3 (2018): 523–62, https://www.brennancenter.org/sites/default/files/publications/images/RLW_HowardLJ_Article.pdf.
In some circumstances, targeted social media use can be both appropriate and productive. As the Brennan Center has noted in the context of the FBI, “public social media posts that express specific and credible threats, when brought to the FBI’s attention, can by themselves be all the evidence necessary to justify opening a preliminary or full investigation, as would any other source of information indicating that a crime is taking place or in the works. Likewise, once the FBI opens a properly predicated investigation, agents may logically conclude that monitoring and recording public or private social media posts would be a fruitful investigative step to gather the evidence necessary for a prosecution.” footnote9_w0NRYNnp6Vr7 9 Michael German and Kaylana Mueller-Hsia, Focusing the FBI: A Proposal for Reform, Brennan Center for Justice, July 28, 2022, 7, https://www.brennancenter.org/our-work/research-reports/focusing-fbi.
When there are no less intrusive means available and when its use is properly limited and narrowly scoped, social media can also help augment preparation for public events, as set out below.
But unbounded social media use by law enforcement can cause considerable harm. As the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy recently recognized, “unchecked social media data collection has been used to threaten people’s opportunities, undermine their privacy, or pervasively track their activity — often without their knowledge or consent.” footnote10_y6DNkb0HbISG 10 Office of Science and Technology Policy, Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights: Making Automated Systems Work for the American People, White House, October 2022, 3, https://www.whitehouse.gov/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/Blueprint-for-an-AI-Bill-of-Rights.pdf. These threats include incursions into constitutionally protected speech and association, disproportionate focus on and repercussions for marginalized communities, and overcollection of irrelevant information. The Department of Justice has advised that even publicly available social media data should not be collected or used indiscriminately by law enforcement. footnote11_wHwWr4jzqNrc 11 Global Advisory Committee, Developing a Policy on the Use of Social Media in Intelligence and Investigative Activities: Guidance and Recommendations, Office of Justice Programs, Department of Justice, February 2013, 6, https://bja.ojp.gov/sites/g/files/xyckuh186/files/media/document/developing_a_policy_on_the_use_of_social_media_in_intelligence_and_inves.pdf.
Moreover, although the issue is understudied, little empirical evidence supports the value of broadscale social media monitoring, footnote12_lsfoOcNMTV4P 12 See German and Mueller-Hsia, Focusing the FBI, 6 (“No one could reasonably suggest that having the FBI employ a team of agents to collect, digitize, and scour for vague indicators of wrongdoing every book, newspaper, magazine, newsletter, press release, and broadcast interview, song, poem, or speech published would be an effective or cost-efficient way to prevent crime or terrorism, especially given that more than half of the violent crime in the U.S. goes unsolved every year. The same holds true for social media.”). and government officials have expressed skepticism about the efficacy of the practice. A 2021 internal review by the Department of Homeland Security Office of the General Counsel, for instance, observed that agents trying to predict threats by collecting social media and other open-source data often instead gathered information on “a broad range of general threats,” ultimately yielding “information of limited value” that included “memes, hyperbole, statements on political organizations and other protected First Amendment speech.” footnote13_xTqvHYbWRGUk 13 Office of the General Counsel, Report on DHS Administrative Review into I&A Open Source Collection and Dissemination Activities During Civil Unrest: Portland, Oregon, June through July 2020, Department of Homeland Security, January 6, 2021, 22, 27, http://cdn.cnn.com/cnn/2021/images/10/01/internal.review.report.20210930.pdf.
This explainer sets out the major risks inherent to law enforcement’s use of social media and then outlines proposed best practices. It aims to contribute to the development of policies that clarify and build appropriate guardrails around social media use by law enforcement.
See, e.g., Marcia Mundt, Karen Ross, and Charla M. Burnett, “Scaling Social Movements Through Social Media: The Case of Black Lives Matter,” Social Media + Society 4, no. 4 (October–December 2018): 1–14, https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/epub/10.1177/2056305118807911; Jane Hu, “The Second Act of Social-Media Activism,” New Yorker, August 3, 2020, https://www.newyorker.com/culture/cultural-comment/the-second-act-of-social-media-activism; and Shira Ovide, “How Social Media Has Changed Civil Rights Protests,” New York Times, updated December 17, 2020, https://www.nytimes.com/2020/06/18/technology/social-media-protests.html.
Black Twitter and Hispanic Twitter (like Asian American Twitter and Feminist Twitter) are monikers coined for the space on Twitter (now X) in which people “discuss issues of concern to themselves and their communities — issues they say either are not covered by mainstream media, or are not covered with the appropriate cultural context.” Deen Freelon et al., How Black Twitter and Other Social Media Communities Interact with Mainstream News, Knight Foundation, February 27, 2018, 38–39, https://knightfoundation.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/02/Marginalized-Twitter-v5.pdf. See also Brooke Auxier, “Social Media Continue to Be Important Political Outlets for Black Americans,” Pew Research Center, December 11, 2020, https://www.pewresearch.org/short-reads/. 2020/12/11/social-media-continue-to-be-important-political-outlets-for-black-americans.
Christian Peña, “How Social Media Is Helping Students of Color Speak Out About Racism on Campus,” PBS NewsHour, September 8, 2020, https://www.pbs.org/newshour/education/how-social-media-is-helping-students-of-color-speak-out-about-racism-on-campus; and Dominique Skye McDaniel, “As Digital Activists, Teens of Color Turn to Social Media to Fight for a More Just World,” Conversation, April 20, 2023, https://theconversation.com/as-digital-activists-teens-of-color-turn-to-social-media-to-fight-for-a-more-just-world-201841.
Freelon et al., How Black Twitter and Other Social Media Communities Interact, 46–47. See also Auxier, “Social Media Continue to Be Important Political Outlets”; Brooke Auxier, “Activism on Social Media Varies by Race and Ethnicity, Age, Political Party,” Pew Research Center, July 13, 2020, https://www.pewresearch.org/short-reads/2020/07/13/activism-on-social-media-varies-by-race-and-ethnicity-age-political-party; and University of Kansas, “Social Media Use Increases Latino Political Participation,” news release, November 5, 2018, https://news.ku.edu/2018/11/02/social-media-use-increases-latino-political-participation.
Matthew D. Luttig and Cathy J. Cohen, “How Social Media Helps Young People — Especially Minorities and the Poor — Get Politically Engaged,” Washington Post, September 9, 2016, https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/monkey-cage/wp/2016/09/09/how-social-media-helps-young-people-especially-minorities-and-the-poor-get-politically-engaged; Auxier, “Social Media Continue to Be Important Political Outlets”; and Auxier, “Activism on Social Media Varies by Race and Ethnicity, Age, Political Party.”
See LexisNexis Risk Solutions, Social Media Use in Law Enforcement: Crime Prevention and Investigative Activities Continue to Drive Usage, November 2014, https://centerforimprovinginvestigations.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/2014-social-media-use-in-law-enforcement-pdf.pdf (documenting multiple use cases of police use of social media).
Carpenter v. U.S., 138 S. Ct. 2206, 2214 (2018) (quoting U.S. v. Di Re, 332 U.S. 581, 595 (1948)) (internal quotation marks omitted). See also Rachel Levinson-Waldman, “Government Access to and Manipulation of Social Media: Legal and Policy Challenges,” Howard Law Journal 61, no. 3 (2018): 523–62, https://www.brennancenter.org/sites/default/files/publications/images/RLW_HowardLJ_Article.pdf.
Michael German and Kaylana Mueller-Hsia, Focusing the FBI: A Proposal for Reform, Brennan Center for Justice, July 28, 2022, 7, https://www.brennancenter.org/our-work/research-reports/focusing-fbi.
Office of Science and Technology Policy, Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights: Making Automated Systems Work for the American People, White House, October 2022, 3, https://www.whitehouse.gov/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/Blueprint-for-an-AI-Bill-of-Rights.pdf.
Global Advisory Committee, Developing a Policy on the Use of Social Media in Intelligence and Investigative Activities: Guidance and Recommendations, Office of Justice Programs, Department of Justice, February 2013, 6, https://bja.ojp.gov/sites/g/files/xyckuh186/files/media/document/developing_a_policy_on_the_use_of_social_media_in_intelligence_and_inves.pdf.
See German and Mueller-Hsia, Focusing the FBI, 6 (“No one could reasonably suggest that having the FBI employ a team of agents to collect, digitize, and scour for vague indicators of wrongdoing every book, newspaper, magazine, newsletter, press release, and broadcast interview, song, poem, or speech published would be an effective or cost-efficient way to prevent crime or terrorism, especially given that more than half of the violent crime in the U.S. goes unsolved every year. The same holds true for social media.”).
Office of the General Counsel, Report on DHS Administrative Review into I&A Open Source Collection and Dissemination Activities During Civil Unrest: Portland, Oregon, June through July 2020, Department of Homeland Security, January 6, 2021, 22, 27, http://cdn.cnn.com/cnn/2021/images/10/01/internal.review.report.20210930.pdf.
Law enforcement officers routinely monitor hashtags, event pages, location data, and other information on social media ahead of public gatherings and political protests to glean information, follow organizers and participants, and develop response plans. footnote1_oj5tLyffPm6g 1 See Brennan Center for Justice, “Civil Rights Concerns About Social Media Monitoring by Law Enforcement,” November 6, 2019, 2, https://www.brennancenter.org/our-work/research-reports/statement-civil-rights-concerns-about-monitoring-social-media-law; and Mundt, Ross, and Burnett, “Scaling Social Movements Through Social Media” (quoting a Black Lives Matter group leader who shared, “I made a Facebook event for a vigil we held for Terence Crutcher. Literally 3 minutes later I got a call from” the local FBI). Some social media monitoring companies tout their ability to create revealing maps of individuals’ online networks, which implicates the right to freedom of association. It also raises questions about the extent to which a person’s ideology can be ascertained via their online presence. footnote2_fFi82MpbsjTZ 2 Rachel Levinson-Waldman and Mary Pat Dwyer, “LAPD Documents Show What One Social Media Surveillance Firm Promises Police,” Brennan Center for Justice, November 17, 2021, https://www.brennancenter.org/our-work/analysis-opinion/lapd-documents-show-what-one-social-media-surveillance-firm-promises. Concerningly, police have even used social media to compile profiles based on First Amendment–protected activities and share them among local, state, and federal agencies — increasing the risk that protesters will later face retaliatory targeting. footnote3_cVr8QkeYdqCb 3 See, e.g., Antonia Noori Farzan, “Memphis Police Used Fake Facebook Account to Monitor Black Lives Matter, Trial Reveals,” Washington Post, August 23, 2018, https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/morning-mix/wp/2018/08/23/memphis-police-used-fake-facebook-account-to-monitor-black-lives-matter-trial-reveals; Alice Speri and Maryam Saleh, “An Immigrant Journalist Faces Deportation as ICE Cracks Down on Its Critics,” Intercept, November 28, 2018, https://theintercept.com/2018/11/28/ice-immigration-arrest-journalist-manuel-duran; and Geofeedia, “Baltimore County Police Department and Geofeedia Partner to Protect the Public During Freddie Gray Riots,” case study, accessed December 27, 2023, http://www.aclunc.org/docs/20161011_geofeedia_baltimore_case_study.pdf (document obtained by the ACLU of Northern California in 2016 through a public records request to the Glendale Police Department in California).
Police in Memphis, Tennessee, for instance, created dossiers on local activists in 2015 and 2016 and shared them with the city council and multiple law enforcement agencies, violating a federal consent decree prohibiting infringement on First Amendment activities. footnote4_anj0c7yfkEIE 4 Brentin Mock, “Memphis Police Spying on Activists Is Worse Than We Thought,” Bloomberg, July 27, 2018, https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2018–07–27/memphis-police-spying-on-black-lives-matter-runs-deep; and Kendrick v. Chandler, No. 76CV0449 (W.D. Tenn. September 14, 1978), order, judgment, and decree (“Kendrick Decree”), https://www.memphispdmonitor.com/_files/ugd/03602e_632d1f4ea1b94b579c559f3489fdaa71.pdf. And in 2022, a social media monitoring vendor under contract with the Los Angeles Police Department (LAPD) alerted the department about a small community education event focused on LAPD’s own online surveillance. footnote5_p4ZelgYe7fKa 5 Rachel Levinson-Waldman, “Documents Show LAPD Monitoring of Community Meeting on . . . LAPD Social Media Monitoring,” Brennan Center for Justice, September 9, 2022, https://www.brennancenter.org/our-work/analysis-opinion/documents-show-lapd-monitoring-community-meeting-lapd-social-media. With no legitimate indication that the event or its attendees posed any threat to public order, the LAPD nevertheless included the event (in which the Brennan Center participated) in internal reports disseminated to several of its divisions.
When police target individuals for surveillance because of their political viewpoints, people may choose to censor their online activity and associations to reduce the risk of governmental monitoring. footnote6_xDYzwegmiSOa 6 Brennan Center for Justice, “Doc Society v. Blinken,” updated February 1, 2024, https://www.brennancenter.org/our-work/court-cases/doc-society-v-blinken; and Knight First Amendment Institute, “Twitter, Reddit File in Support of Lawsuit Challenging U.S. Government’s Social Media Registration Requirement for Visa Applicants,” news release, May 29, 2020, https://knightcolumbia.org/content/twitter-reddit-file-in-support-of-lawsuit-challenging-us-governments-social-media-registration-requirement-for-visa-applicants?_preview_=4d450decff. Research bears this out: one study showed that people are less willing to share non-majority views online when reminded that the government monitors these activities. footnote7_elOvnyxivW4z 7 Kaveh Waddell, “How Surveillance Stifles Dissent on the Internet,” Atlantic, April 5, 2016, https://www.theatlantic.com/technology/archive/2016/04/how-surveillance-mutes-dissent-on-the-internet/476955. Remarkably, this effect was actually more prominent among people who thought they had nothing to hide.
This chilling effect undermines social media’s ability to serve as the new public square and weakens civic connections, particularly for those groups most likely to be targeted online. One environmental activist who had been targeted by police due in part to her online activity described it thus: “Once I realized we were being surveilled and information was being used against us in different ways, I stopped sharing and making these kinds of posts. . . . It made me think, am I safe to share things publicly? Photos of my children? Life events? Political beliefs?” footnote8_tpFKsGjUvIl0 8 Gabriella Sanchez and Rachel Levinson-Waldman, “Police Social Media Monitoring Chills Activism,” Brennan Center for Justice, November 18, 2022, https://www.brennancenter.org/our-work/analysis-opinion/police-social-media-monitoring-chills-activism.
Racial and ethnic bias in policing, a well-recognized phenomenon, seeps into online monitoring as well. Documented examples abound of police using social media to target activists of color and groups seeking racial justice. The Boston Police Department, for example, enlisted a social media monitoring tool to track mentions of the terms Black Lives Matter and Muslim Lives Matter, among others. footnote9_jimBj4HXn7UY 9 Nasser Eledroos and Kade Crockford, “Social Media Monitoring in Boston: Free Speech in the Crosshairs,” ACLU of Massachusetts, 2018, https://privacysos.org/social-media-monitoring-boston-free-speech-crosshairs. Similarly, the LAPD employed an online surveillance tool to monitor hashtags such as #BlackLivesMatter and #SayHerName, along with tweets about victims of police killings, including Sandra Bland and Tamir Rice. footnote10_x2sS5saQk64t 10 Mary Pat Dwyer, “LAPD Documents Reveal Use of Social Media Monitoring Tools,” Brennan Center for Justice, September 8, 2021, https://www.brennancenter.org/our-work/analysis-opinion/lapd-documents-reveal-use-social-media-monitoring-tools. And during the 2020 racial justice demonstrations following the deaths of George Floyd and Breonna Taylor, law enforcement agencies around the country turned to a tool from the artificial intelligence (AI) surveillance company Dataminr to monitor protestors through their social media activity. footnote11_coMn0EUuyldC 11 Sam Biddle, “Police Surveilled George Floyd Protests with Help from Twitter-Affiliated Startup Dataminr,” Intercept, July 9, 2020, https://theintercept.com/2020/07/09/twitter-dataminr-police-spy-surveillance-black-lives-matter-protests.
When it comes to police surveillance, what happens online does not always stay online. The Fresno Police Department in California has used a tool called Beware that captures social media data to help calculate individuals’ “threat scores” and shared that information with operators dispatching officers on calls, posing the risk that officers might arrive ready to shoot or with a SWAT team in tow if social media inaccurately flagged someone as a threat. footnote12_umdh3PgAqr3B 12 Justin Jouvenal, “The New Way Police Are Surveilling You: Calculating Your Threat ‘Score,’” Washington Post, January 10, 2016, https://www.washingtonpost.com/local/public-safety/the-new-way-police-are-surveilling-you-calculating-your-threat-score/2016/01/10/e42bccac-8e15–11e5-baf4-bdf37355da0c_story.html.
Images and other data gleaned from social media also feed the sweeping reach of gang databases, footnote13_hH9UQ5yQbpt2 13 See statement of Chief Dermot Shea, New York City Police Department, before the New York City Council Committee on Public Safety, June 13, 2018, 4, https://jjie.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Gang-Testimony-Public-Version.docx. which typically consist almost entirely of individuals of color and are plagued with inaccuracies, as reported by oversight offices in multiple big-city police departments. footnote14_vVQkrWy4im2k 14 See Matt Masterson, “Gang Database ‘Strains Police-Community Relations’ City Watchdog Says,” WTTW (PBS Chicago), April 11, 2019, https://news.wttw.com/2019/04/11/gang-database-strains-police-community-relations-city-watchdog-says (describing a 2019 Chicago Police Department inspector general report finding that 95 percent of the individuals in Chicago’s gang database were Black or Latino and that the database was filled with poor-quality data and suffered from a lack of sufficient controls, procedural protections, and transparency); City of Chicago Office of Inspector General, Follow-Up Inquiry on the Chicago Police Department’s “Gang Database,” March 2021, 18, https://igchicago.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/OIG-Follow-Up-Inquiry-on-the-Chicago-Police-Departments-Gang-Database.pdf (finding that the Chicago Police Department had “made minimal progress” toward a functional database, thereby undermining crime-fighting efforts and misleading the public); and KCAL (CBS Los Angeles), “DOJ Revokes LAPD Access to CalGang Database After Gang Framing Scandal,” July 14, 2020, https://www.cbsnews.com/losangeles/news/doj-revokes-lapd-access-to-calgang-database-after-gang-framing-scandal/ (reporting that LAPD was barred from using the California gang database after revelations that officers had entered inaccurate information into database to frame people as gang members). According to an April 2023 report released by the New York City Police Department (NYPD) inspector general, individuals can be added to the NYPD’s gang database based solely on social media content when it amounts to “self-admission” of one’s membership to a gang. footnote15_isMFeehsZjx0 15 NYPD Office of Inspector General (OIG), An Investigation into NYPD’s Criminal Group Database, April 2023, 25, https://www.nyc.gov/assets/doi/reports/pdf/2023/16CGDRpt.Release04.18.2023.pdf. “Self-admission” is broadly defined to include “an individual’s use of language, symbols, pictures, or colors associated with a criminal group.” footnote16_jPPFiIlopz6f 16 NYPD OIG, Investigation into NYPD’s Criminal Group Database, 5. Being photographed with a known gang member — even in a context has nothing to do with gang activity — or the use of a specific emoji is sufficient. And inclusion in a gang database has real consequences. Individuals listed as gang members may face increased bail and police escalation of routine traffic stops. footnote17_hMZ9VC8tZcZW 17 Josmar Trujillo and Alex S. Vitale, Gang Takedowns in the De Blasio Era: The Dangers of “Precision Policing,” Policing and Social Justice Project, City University of New York, 2019, 7, 12, 15, https://static1.squarespace.com/static/5de981188ae1bf14a94410f5/t/5df14904887d561d6cc9455e/1576093963895/2019+New+York+City+Gang+Policing+Report+-+FINAL%29.pdf. While the NYPD OIG stated that it did not find evidence of specific harms caused by inclusion in the database, it also declined to investigate potential harms, which it said would have been difficult to assess and outside the scope of its report. NYPD OIG, Investigation into NYPD’s Criminal Group Database, 3, 21–22. Men of color experience these harms most acutely: 99 percent of individuals included in the NYPD’s gang database are Black or Latino; Black men comprise the vast majority. footnote18_cMzddRHw0Tys 18 NYPD OIG, Investigation into NYPD’s Criminal Group Database, 34. Furthermore, online surveillance can reinforce policing biases even when the police themselves are not doing the monitoring. Dataminr employees have reported that online searches for gang members and gang-related activities to include in the company’s news alert service for police and other public-sector clients focused predominantly on users of color, reflecting their perceptions of both the company’s orders and law enforcement’s appetite for “threat fodder.” footnote19_rnd81P7UwP8U 19 Sam Biddle, “Twitter Surveillance Startup Targets Communities of Color for Police,” Intercept, October 21, 2020, https://theintercept.com/2020/10/21/dataminr-twitter-surveillance-racial-profiling.
Political inclinations also affect how law enforcement officers view online activity. Numerous online posts suggested that violence would occur at the U.S. Capitol on January 6, 2021, yet law enforcement seemed to minimize the threat, failing to take the threat seriously enough to plan for an attack. footnote20_rtLaWhAtusUr 20 See Justin Hendrix, “Facebook Provided Warning to FBI Before January 6, GAO Report Reveals,” Just Security (blog), May 5, 2022, https://www.justsecurity.org/81384/facebook-provided-warning-to-fbi-before-january-6-gao-report-reveals; and S. Comm. on Homeland Security and Governmental Affairs, Planned in Plain Sight: A Review of the Intelligence Failures in Advance of January 6th, 2021, June 2023, https://www.hsgac.senate.gov/wp-content/uploads/230627_HSGAC-Majority-Report_Jan-6-Intel.pdf. Instead, in the months leading up to the attack, federal law enforcement focused on framing racial justice protests as being instigated by antifa (or anti-fascists), in line with the Donald Trump administration’s messaging and reflecting prevalent law enforcement sympathies. footnote21_gAE3Mb7AKbF4 21 Curtis Waltman, “In California, Homeland Security Continues to Argue that Antifa, Not White Supremacists, Pose ‘The Greatest Threat to Public Safety,’” Muckrock, April 10, 2018, https://www.muckrock.com/news/archives/2018/apr/10/dhss-antifa-neonazi-CA-rundown; and Will Carless, “As FBI Probed Jan. 6, Many Agents Sympathized with Insurrection, According to Newly Released Email,” USA Today, October 15, 2022, https://www.usatoday.com/story/news/nation/2022/10/15/jan-6-insurrection-fbi-agents-paul-abbate-warning/10498351002. See also Michael German, Hidden in Plain Sight: Racism, White Supremacy, and Far-Right Militancy in Law Enforcement, Brennan Center for Justice, August 27, 2020, https://www.brennancenter.org/our-work/research-reports/hidden-plain-sight-racism-white-supremacy-and-far-right-militancy-law. This history suggests that even if widespread social media surveillance were effective in flagging threats, neither its use nor its application will be equitable.
Accurately assessing the meanings of posts, pictures, music, videos, and other forms of expression and communication on social media is notoriously challenging. Individuals use in-group slang, and both law enforcement personnel and algorithmic tools may fail to recognize sarcasm, satire, or hyperbole. Trying to interpret posts by young people, who often use memes and pop culture references that may be inscrutable to outsiders, can intensify these challenges. This effect is likely to be heightened for young people of color and immigrant youths, who are more heavily policed and more susceptible to inaccurate or biased presumptions that gestures, clothing, and other characteristics viewed online indicate gang activity or other criminal behavior. footnote22_vstsDg0Xl904 22 See Kianna Ortiz and Ananya Roy, All Eyes on Us, Youth Justice Board, Center for Court Innovation, January 2020, 11–13, https://www.innovatingjustice.org/sites/default/files/media/document/2020/Report_YJB_06302020.pdf.[/fn] The Immigrant Legal Resource Center, for instance, reported on the deportation of a mentally disabled teenager that was evidently based in large part on Facebook pictures of the teen wearing a Chicago Bulls t-shirt, Nike shoes, and blue clothes, including a shirt that was part of his required school uniform — presumed to be evidence of membership in the MS-13 gang.Laila L. Hlass and Rachel Prandini, Deportation by Any Means Necessary: How Immigration Officials Are Labeling Immigrant Youth as Gang Members, Immigrant Legal Resource Center, May 21, 2018, 3, https://www.ilrc.org/sites/default/files/resources/deport_by_any_means_nec-20180521.pdf. See also Philip Marcelo, “Court Decision Deals Blow to Boston Police Gang Database,” Boston.com, January 12, 2022, https://www.boston.com/news/local-news/2022/01/12/court-decision-deals-blow-to-boston-police-gang-database (describing how a federal appeals court overturned the immigration board’s decision to deport the teenager after determining that the Boston Police Department’s gang database relied on “an erratic point system built on unsubstantiated inferences” and did not contain compelling evidence of gang membership or association).
Critically, police and others in positions of authority may be more apt to perceive a social media post as dangerous based on the speaker or their viewpoint. For example, police in Kansas arrested a Black teenager in 2020 on charges that he had contributed to inciting a riot through a Snapchat post; in fact, his post denounced violence rumored to be coming toward his hometown. footnote23_tzqOABl9DVcg 23 Amy Renee Leiker, “Outcry Follows Arrest of 2 Men over Social Media Post That Urged Violence in Wichita Area,” Wichita Eagle, June 8, 2020, https://www.kansas.com/news/local/crime/article243267626.html; and Quiaana Pinkston, “Justice for Rashawn Mayes,” GoFundMe, June 4, 2020, https://www.gofundme.com/f/justice-for-rashawn-mayes. In another instance, the former head of the civil rights division at the Oregon Department of Justice was wrongly identified as a threat — and was ultimately forced out of his job — because he tweeted graphics from a popular Public Enemy album that police misinterpreted as menacing. footnote24_u7dYSNh5AVn3 24 John Sepulvado, “Black Lives Matter Report: Tweet Quoting Public Enemy Prompted DOJ Investigation,” Oregon Public Broadcasting, April 11, 2016, https://www.opb.org/news/article/black-lives-matter-report-tweet-quoting-public-enemy-prompted-doj-investigation. That tweet and others were discovered and flagged for DOJ officials by an investigator using a digital surveillance tool trained to look for social media mentions of “Black Lives Matter” and “KKK,” among other terms.
A person’s social media connections can reflect everything from close relationships to passing acquaintanceships. An outside observer may struggle to accurately interpret the strength or depth of those associations. People may feel social pressure to connect with family members, colleagues, professional acquaintances, or classmates online, and they may feel compelled to interact with their connections by commenting on or liking a post whether or not a relationship is remote. These dynamics make it particularly fraught to ascribe criminal intent or activity to an individual based on online linkages, which may be superficial or, even if they do reflect an actual relationship, may not signify participation in illegal activity.
The presumption that online proximity necessarily reflects a real-life affiliation can have tragic consequences, especially for young people of color. In one example, a Black New York City teen spent more than a year at the Rikers Island correctional facility, much of it in solitary confinement, based largely on the district attorney’s assessment that he was a member of a criminal gang. footnote25_aROZ4koujkGG 25 Ben Popper, “How the NYPD Is Using Social Media to Put Harlem Teens Behind Bars,” Verge, December 10, 2014, https://www.theverge.com/2014/12/10/7341077/nypd-harlem-crews-social-media-rikers-prison. The district attorney relied on Facebook photos of the teen with members of a local crew (a group of young people, typically young men, loosely affiliated by block or housing development) and several posts from crew members that he had liked. In fact, the teen was simply connected to crew members because they were his neighbors and family members. footnote26_yNvi2Io43CxO 26 Popper, “How the NYPD Is Using Social Media.”
Also troubling is the law enforcement practice of feeding pictures drawn from social media into facial recognition programs to generate leads and identify possible subjects. These algorithms have a documented history of performing less accurately on people with darker skin, and women of color in particular. footnote27_wAgG8BqXQX6w 27 See Malachi Barrett, “How Authorities Use Social Media to Aid Investigations,” Government Technology, August 11, 2021, https://www.govtech.com/news/how-authorities-use-social-media-to-aid-investigations. At least six people in four states (Georgia, Maryland, Michigan, and New Jersey) are known to have been wrongfully arrested because they were misidentified by facial recognition software. Five of them were Black men; one was a Black woman. footnote28_k6BMueW690qo 28 Kashmir Hill, “Eight Months Pregnant and Arrested After False Facial Recognition Match,” New York Times, August 6, 2023, https://www.nytimes.com/2023/08/06/business/facial-recognition-false-arrest.html; Katie Hawkinson, “In Every Reported Case Where Police Mistakenly Arrested Someone Using Facial Recognition, That Person Has Been Black,” Business Insider, August 6, 2023, https://www.businessinsider.com/in-every-reported-false-arrests-based-on-facial-recognition-that-person-has-been-black-2023–8; Khari Johnson, “Face Recognition Software Led to His Arrest. It Was Dead Wrong,” Wired, February 28, 2023, https://www.wired.com/story/face-recognition-software-led-to-his-arrest-it-was-dead-wrong; and Khari Johnson, “How Wrongful Arrests Based on AI Derailed 3 Men’s Lives,” Wired, March 7, 2022, https://www.wired.com/story/wrongful-arrests-ai-derailed-3-mens-lives.
Social media can even be used for misdirection, further undermining its ostensible utility for law enforcement. In one such instance, a young man posted multiple photos of himself in different locations holding a pistol to convey the impression that he was ready for a violent confrontation. In reality, the man took the photos in a single afternoon with a borrowed gun and posted them over time to suggest that he typically had the weapon with him. He told a sociologist conducting fieldwork in his neighborhood that he did not carry the weapon around, let alone plan to use it; he simply wanted people to assume that he was armed to feel more secure in public. footnote29_f98Cupb6zig0 29 Melissa De Witte, “Gang-Associated Youth Avoid Violence by Acting Tough Online, Stanford Sociologist Finds,” Stanford News Service, May 1, 2019, https://news.stanford.edu/press-releases/2019/05/01/gangs-use-social-media. The same sociologist, Stanford University professor Forrest Stuart, has documented the ways in which Black youths who drive Chicago’s drill music culture promote a tough and sometimes violent image online that, by design, often vastly overstates the actual levels of violence in their daily lives. footnote30_iyNJ67QKWHeX 30 Forrest Stuart, Ballad of the Bullet: Gangs, Drill Music, and the Power of Online Infamy (Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 2020).
When lies reinforce existing biases, the risk that law enforcement or intelligence agencies will be duped into acting on fake posts is amplified. In 2020, the Maine fusion center disseminated FBI and DHS reports to local law enforcement agencies warning of potential violence at anti–police brutality demonstrations. These warnings turned out to be based on fake social media posts by right-wing provocateurs. footnote31_y4qRWVlplgNr 31 Nathan Bernard, “Maine Spy Agency Spread Far-Right Rumors of BLM Protest Violence,” Mainer, July 7, 2020, https://web.archive.org/web/20220218053843/https://mainernews.com/maine-spy-agency-spread-far-right-rumors-of-blm-protest-violence.[/fn] And online platforms can supercharge the reach of inaccurate information, as when a young South Asian student was wrongly identified as one of the Boston Marathon bombers, devastating his family.See Jay Caspian King, “Should Reddit Be Blamed for the Spreading of a Smear?,” New York Times, July 25, 2013, https://www.nytimes.com/2013/07/28/magazine/should-reddit-be-blamed-for-the-spreading-of-a-smear.html; and NPR, “How Social Media Smeared a Missing Student as a Terrorism Suspect,” April 18, 2016, https://www.npr.org/sections/codeswitch/2016/04/18/474671097/how-social-media-smeared-a-missing-student-as-a-terrorism-suspect.
Many third-party social media surveillance tools utilize keyword lists to flag threats for law enforcement. Yet these tools struggle to account for variables like tone, speaker, and context. footnote32_dVb7Wys3No3F 32 Natasha Duarte, Emma Llansó, and Anna Loup, Mixed Messages? The Limits of Automated Social Media Content Analysis, Center for Democracy and Technology, November 2017, 3, https://cdt.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/Mixed-Messages-Paper.pdf. Automated programs may simply report all posts containing flagged words, leading to piles of irrelevant reports. Police in Jacksonville, Florida, learned that rather than uncovering early threat indicators, flagging the word bomb elicited posts describing first-rate pizza or beer as “the bomb.” footnote33_vvOGxgDo5k30 33 Ben Conarck, “Sheriff’s Office’s Social Media Tool Regularly Yielded False Alarms,” Jacksonville.com, May 30, 2017, https://www.jacksonville.com/story/news/crime/2017/05/30/sheriff-s-office-s-social-media-tool-regularly-yielded-false/15757269007. School officials who have purchased monitoring software to scour students’ social media accounts have ultimately found that those tools offered insufficient value as well. footnote34_p97CqvioIGDY 34 Lizzie O’Leary, “Why Expensive Social Media Monitoring Has Failed to Protect Schools,” Slate, June 4, 2022, https://slate.com/technology/2022/06/social-media-monitoring-software-schools-safety.html. Notably, these kinds of products also violate the major platforms’ policies, which prohibit developers from using their data for surveillance purposes. footnote35_neyLhwIPcL39 35 Meta, “Meta Platform Terms,” updated April 25, 2023, https://developers.facebook.com/terms/dfc_platform_terms/#datause; and X Corp., “Developer Terms: More About Restricted Uses of the Twitter APIs,” accessed December 27, 2023, https://developer.twitter.com/en/developer-terms/more-on-restricted-use-cases.
Moreover, natural language processing tools that are trained in one language can have trouble accurately interpreting other ones. footnote36_e8CFgadaVcwn 36 See Duarte, Llansó, and Loup, Mixed Messages?, 14–15. In one example, Israeli police held and questioned a man who had posted the greeting “good morning” in Arabic; an automated tool mistranslated it into Hebrew as “attack them.” footnote37_m78MBj5xvKKt 37 Dirk Hovy, “Demographic Factors Improve Classification Performance,” Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 7th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing 1 (July 2015): 752–62, https://aclanthology.org/P15–1073.pdf. This bias can also surface when a system attempts to understand dialects for which training data was lacking. A 2017 study of natural language processing tools found that they miscategorized African American Vernacular English (AAVE) as non-English. One system incorrectly identified it as Danish with 99.9 percent confidence. footnote38_lPtjpoYDWtsI 38 Duarte, Llansó, and Loup, Mixed Messages?, 15. A more recent study demonstrated that even some of the more sophisticated large language models can falter considerably in many non-English languages. footnote39_rDJkHoLtBZV5 39 See Gabriel Nicholas and Aliya Bhatia, Lost in Translation: Large Language Models in Non-English Content Analysis, Center for Democracy and Technology, May 2023, https://cdt.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/non-en-content-analysis-primer-051223–1203.pdf.
Finally, the use of undercover accounts or false identities on social media presents particular opportunities for mischief and privacy intrusions. Alias identities can be used to trick people into accepting connections they would not have permitted in real life, allowing law enforcement officers to see a wealth of information that they would not otherwise be privy to — including posts, pictures, and information about friends and family members — and even exchange and view private communications. In-person covert activity raises these same concerns but comes with built-in limitations: an officer interacting in person cannot easily pretend to be a target’s childhood best friend, or someone of a different race or ethnicity, or multiple people. None of these limitations applies to online covert activity.
The relative ease of purporting to be more than one person online implicates the Supreme Court’s growing recognition that effortless surveillance may “alter the relationship between citizen and government in a way that is inimical to democratic society.” footnote40_sswgxAhDvd8x 40 U.S. v. Jones, 565 U.S. 400, 416 (2012) (Sotomayor, J., concurring) (quoting U.S. v. Cuevas-Perez, 640 F.3d 272, 285 (7th Cir. 2011)) (internal quotation marks omitted). Technological tools can populate fake accounts with a sufficient range of interests and connections to look legitimate. Some digital monitoring companies even create fake accounts in bulk, using them to scrape millions of data points from public social media accounts. This practice violates Facebook’s and Instagram’s policies, but as long as the surveillance companies evade detection, police departments can buy licenses to use these products to gather information on individuals and groups anonymously. footnote41_pfK3uSvy1Vyr 41 Jonathan Vanian, “Meta Sues Voyager Labs, Saying It Created Fake Accounts to Scrape User Data,” CNBC, January 12, 2023, https://www.cnbc.com/2023/01/12/meta-sues-voyager-labs-over-scraping-user-data.html; and Rachel Levinson-Waldman and Gabriella Sanchez, “Meta Sues Surveillance Firm That Worked with Police,” Brennan Center for Justice, January 26, 2023, https://www.brennancenter.org/our-work/analysis-opinion/meta-sues-surveillance-firm-worked-police. According to an amended complaint filed by Meta, Voyager continued to create fake accounts and scrape data from hundreds of thousands of Facebook users even after Meta served the company with multiple cease-and-desist letters and filed suit.
At the same time, while many police departments have public-facing policies permitting personnel to use covert accounts in at least some circumstances, only a fraction of those policies incorporate baseline limitations on online undercover activity — such as requirements that accounts be used only when reasonable articulable suspicion of a crime exists or that they be subject to regular supervisory review — let alone the more robust restraints set out below. footnote42_wnnjOvxi3eOx 42 Rachel Levinson-Waldman, “Directory of Police Department Social Media Policies,” Brennan Center for Justice, updated February 7, 2024, https://www.brennancenter.org/our-work/research-reports/directory-police-department-social-media-policies. These loose controls have led to abuses: the Memphis Police Department used an undercover Facebook account to target racial justice activists, footnote43_gIZuKNj45pUK 43 Antonia Noori Farzan, “Memphis Police Used Fake Facebook Account to Monitor Black Lives Matter, Trial Reveals,” Washington Post, August 23, 2018, https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/morning-mix/wp/2018/08/23/memphis-police-used-fake-facebook-account-to-monitor-black-lives-matter-trial-reveals. and the NAACP sued the city of Minneapolis for alleged discriminatory use of undercover social media accounts to target activists of color. footnote44_gCqrCyR6nl2F 44 David Schuman, “NAACP Files Lawsuit Against Minneapolis for Alleged Discriminatory Social Media Surveillance,” WCCO (CBS News Minnesota), updated April 26, 2023, https://www.cbsnews.com/minnesota/news/naacp-files-lawsuit-against-minneapolis; and Minnesota Department of Human Rights v. City of Minneapolis, 27CV234177 (Minn. Dist. Ct. March 31, 2023), https://mn.gov/mdhr/assets/Court%20Enforceable%20Agreement_tcm1061–571942.pdf. The lawsuit resulted in a consent decree between the city and the Minnesota Department of Human Rights that contains new procedural and oversight mechanisms for undercover account use. footnote45_vgN4lFLzC5SE 45 Jonah Kaplan, “MPD Settlement Agreement Approved, Altering the Future of Policing in Minneapolis,” WCCO (CBS News Minnesota), March 31, 2023, https://www.cbsnews.com/minnesota/news/minneapolis-state-officials-unanimously-approve-court-enforceable-settlement-agreement. Limitations for offline undercover operations have been an important part of consent decrees in places like New York City, where police have a long history of targeting political groups seeking racial justice. See Hamid Hassan Raza v. City of New York, No. 13CV3448 (E.D.N.Y. March 20, 2017), stipulation of settlement and order, exhibit A, 16–17, https://static1.squarespace.com/static/5c1bfc7eee175995a4ceb638/t/5d2f69ca7df2d700014089b8/1563388365355/Revised+Handschu+Guidelines.pdf.
Also worth noting is that use of a false name directly violates Facebook’s terms of service. The company’s head of civil rights has emphasized that there is no exception to this policy for the police, and it has sent sharp letters of rebuke to both the Memphis and Los Angeles police departments, And Meta filed suit in 2022 against a company that uses fake accounts to scrape data from Facebook users and has advertised its services to the government. footnote46_f6MvjreqGqgh 46 Roy Austin, vice president of civil rights and deputy general counsel, Meta, letter to Michel Moore, chief, Los Angeles Police Department, November 11, 2021, https://about.fb.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/LAPD-Letter.pdf; Andrea Kirkpatrick, director and associate general counsel for security, Facebook, letter to Michael Rallings, director, Memphis Police Department, September 19, 2018, https://www.eff.org/document/facebook-letter-memphis-police-department-fake-accounts; and Levinson-Waldman and Sanchez, “Meta Sues Surveillance Firm That Worked with Police.” See also Mara Hvistendahl, “FBI Provides Chicago Police with Fake Online Identities for ‘Social Media Exploitation’ Team,” Intercept, May 20, 2022, https://theintercept.com/2022/05/20/chicago-police-fbi-social-media-surveillance-fake.
See Brennan Center for Justice, “Civil Rights Concerns About Social Media Monitoring by Law Enforcement,” November 6, 2019, 2, https://www.brennancenter.org/our-work/research-reports/statement-civil-rights-concerns-about-monitoring-social-media-law; and Mundt, Ross, and Burnett, “Scaling Social Movements Through Social Media” (quoting a Black Lives Matter group leader who shared, “I made a Facebook event for a vigil we held for Terence Crutcher. Literally 3 minutes later I got a call from” the local FBI).
Rachel Levinson-Waldman and Mary Pat Dwyer, “LAPD Documents Show What One Social Media Surveillance Firm Promises Police,” Brennan Center for Justice, November 17, 2021, https://www.brennancenter.org/our-work/analysis-opinion/lapd-documents-show-what-one-social-media-surveillance-firm-promises.
See, e.g., Antonia Noori Farzan, “Memphis Police Used Fake Facebook Account to Monitor Black Lives Matter, Trial Reveals,” Washington Post, August 23, 2018, https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/morning-mix/wp/2018/08/23/memphis-police-used-fake-facebook-account-to-monitor-black-lives-matter-trial-reveals; Alice Speri and Maryam Saleh, “An Immigrant Journalist Faces Deportation as ICE Cracks Down on Its Critics,” Intercept, November 28, 2018, https://theintercept.com/2018/11/28/ice-immigration-arrest-journalist-manuel-duran; and Geofeedia, “Baltimore County Police Department and Geofeedia Partner to Protect the Public During Freddie Gray Riots,” case study, accessed December 27, 2023, http://www.aclunc.org/docs/20161011_geofeedia_baltimore_case_study.pdf (document obtained by the ACLU of Northern California in 2016 through a public records request to the Glendale Police Department in California).
Brentin Mock, “Memphis Police Spying on Activists Is Worse Than We Thought,” Bloomberg, July 27, 2018, https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2018–07–27/memphis-police-spying-on-black-lives-matter-runs-deep; and Kendrick v. Chandler, No. 76CV0449 (W.D. Tenn. September 14, 1978), order, judgment, and decree (“Kendrick Decree”), https://www.memphispdmonitor.com/_files/ugd/03602e_632d1f4ea1b94b579c559f3489fdaa71.pdf.
Rachel Levinson-Waldman, “Documents Show LAPD Monitoring of Community Meeting on . . . LAPD Social Media Monitoring,” Brennan Center for Justice, September 9, 2022, https://www.brennancenter.org/our-work/analysis-opinion/documents-show-lapd-monitoring-community-meeting-lapd-social-media.
Brennan Center for Justice, “Doc Society v. Blinken,” updated February 1, 2024, https://www.brennancenter.org/our-work/court-cases/doc-society-v-blinken; and Knight First Amendment Institute, “Twitter, Reddit File in Support of Lawsuit Challenging U.S. Government’s Social Media Registration Requirement for Visa Applicants,” news release, May 29, 2020, https://knightcolumbia.org/content/twitter-reddit-file-in-support-of-lawsuit-challenging-us-governments-social-media-registration-requirement-for-visa-applicants?_preview_=4d450decff.
Gabriella Sanchez and Rachel Levinson-Waldman, “Police Social Media Monitoring Chills Activism,” Brennan Center for Justice, November 18, 2022, https://www.brennancenter.org/our-work/analysis-opinion/police-social-media-monitoring-chills-activism.
Nasser Eledroos and Kade Crockford, “Social Media Monitoring in Boston: Free Speech in the Crosshairs,” ACLU of Massachusetts, 2018, https://privacysos.org/social-media-monitoring-boston-free-speech-crosshairs.
Mary Pat Dwyer, “LAPD Documents Reveal Use of Social Media Monitoring Tools,” Brennan Center for Justice, September 8, 2021, https://www.brennancenter.org/our-work/analysis-opinion/lapd-documents-reveal-use-social-media-monitoring-tools.
Sam Biddle, “Police Surveilled George Floyd Protests with Help from Twitter-Affiliated Startup Dataminr,” Intercept, July 9, 2020, https://theintercept.com/2020/07/09/twitter-dataminr-police-spy-surveillance-black-lives-matter-protests.
See statement of Chief Dermot Shea, New York City Police Department, before the New York City Council Committee on Public Safety, June 13, 2018, 4, https://jjie.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Gang-Testimony-Public-Version.docx.
See Matt Masterson, “Gang Database ‘Strains Police-Community Relations’ City Watchdog Says,” WTTW (PBS Chicago), April 11, 2019, https://news.wttw.com/2019/04/11/gang-database-strains-police-community-relations-city-watchdog-says (describing a 2019 Chicago Police Department inspector general report finding that 95 percent of the individuals in Chicago’s gang database were Black or Latino and that the database was filled with poor-quality data and suffered from a lack of sufficient controls, procedural protections, and transparency); City of Chicago Office of Inspector General, Follow-Up Inquiry on the Chicago Police Department’s “Gang Database,” March 2021, 18, https://igchicago.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/OIG-Follow-Up-Inquiry-on-the-Chicago-Police-Departments-Gang-Database.pdf (finding that the Chicago Police Department had “made minimal progress” toward a functional database, thereby undermining crime-fighting efforts and misleading the public); and KCAL (CBS Los Angeles), “DOJ Revokes LAPD Access to CalGang Database After Gang Framing Scandal,” July 14, 2020, https://www.cbsnews.com/losangeles/news/doj-revokes-lapd-access-to-calgang-database-after-gang-framing-scandal/ (reporting that LAPD was barred from using the California gang database after revelations that officers had entered inaccurate information into database to frame people as gang members).
NYPD Office of Inspector General (OIG), An Investigation into NYPD’s Criminal Group Database, April 2023, 25, https://www.nyc.gov/assets/doi/reports/pdf/2023/16CGDRpt.Release04.18.2023.pdf.
Josmar Trujillo and Alex S. Vitale, Gang Takedowns in the De Blasio Era: The Dangers of “Precision Policing,” Policing and Social Justice Project, City University of New York, 2019, 7, 12, 15, https://static1.squarespace.com/static/5de981188ae1bf14a94410f5/t/5df14904887d561d6cc9455e/1576093963895/2019+New+York+City+Gang+Policing+Report+-+FINAL%29.pdf. While the NYPD OIG stated that it did not find evidence of specific harms caused by inclusion in the database, it also declined to investigate potential harms, which it said would have been difficult to assess and outside the scope of its report. NYPD OIG, Investigation into NYPD’s Criminal Group Database, 3, 21–22.
Sam Biddle, “Twitter Surveillance Startup Targets Communities of Color for Police,” Intercept, October 21, 2020, https://theintercept.com/2020/10/21/dataminr-twitter-surveillance-racial-profiling.
See Justin Hendrix, “Facebook Provided Warning to FBI Before January 6, GAO Report Reveals,” Just Security (blog), May 5, 2022, https://www.justsecurity.org/81384/facebook-provided-warning-to-fbi-before-january-6-gao-report-reveals; and S. Comm. on Homeland Security and Governmental Affairs, Planned in Plain Sight: A Review of the Intelligence Failures in Advance of January 6th, 2021, June 2023, https://www.hsgac.senate.gov/wp-content/uploads/230627_HSGAC-Majority-Report_Jan-6-Intel.pdf.
Curtis Waltman, “In California, Homeland Security Continues to Argue that Antifa, Not White Supremacists, Pose ‘The Greatest Threat to Public Safety,’” Muckrock, April 10, 2018, https://www.muckrock.com/news/archives/2018/apr/10/dhss-antifa-neonazi-CA-rundown; and Will Carless, “As FBI Probed Jan. 6, Many Agents Sympathized with Insurrection, According to Newly Released Email,” USA Today, October 15, 2022, https://www.usatoday.com/story/news/nation/2022/10/15/jan-6-insurrection-fbi-agents-paul-abbate-warning/10498351002. See also Michael German, Hidden in Plain Sight: Racism, White Supremacy, and Far-Right Militancy in Law Enforcement, Brennan Center for Justice, August 27, 2020, https://www.brennancenter.org/our-work/research-reports/hidden-plain-sight-racism-white-supremacy-and-far-right-militancy-law.
See Kianna Ortiz and Ananya Roy, All Eyes on Us, Youth Justice Board, Center for Court Innovation, January 2020, 11–13, https://www.innovatingjustice.org/sites/default/files/media/document/2020/Report_YJB_06302020.pdf.[/fn] The Immigrant Legal Resource Center, for instance, reported on the deportation of a mentally disabled teenager that was evidently based in large part on Facebook pictures of the teen wearing a Chicago Bulls t-shirt, Nike shoes, and blue clothes, including a shirt that was part of his required school uniform — presumed to be evidence of membership in the MS-13 gang. Laila L. Hlass and Rachel Prandini, Deportation by Any Means Necessary: How Immigration Officials Are Labeling Immigrant Youth as Gang Members, Immigrant Legal Resource Center, May 21, 2018, 3, https://www.ilrc.org/sites/default/files/resources/deport_by_any_means_nec-20180521.pdf. See also Philip Marcelo, “Court Decision Deals Blow to Boston Police Gang Database,” Boston.com, January 12, 2022, https://www.boston.com/news/local-news/2022/01/12/court-decision-deals-blow-to-boston-police-gang-database (describing how a federal appeals court overturned the immigration board’s decision to deport the teenager after determining that the Boston Police Department’s gang database relied on “an erratic point system built on unsubstantiated inferences” and did not contain compelling evidence of gang membership or association).
Amy Renee Leiker, “Outcry Follows Arrest of 2 Men over Social Media Post That Urged Violence in Wichita Area,” Wichita Eagle, June 8, 2020, https://www.kansas.com/news/local/crime/article243267626.html; and Quiaana Pinkston, “Justice for Rashawn Mayes,” GoFundMe, June 4, 2020, https://www.gofundme.com/f/justice-for-rashawn-mayes.
John Sepulvado, “Black Lives Matter Report: Tweet Quoting Public Enemy Prompted DOJ Investigation,” Oregon Public Broadcasting, April 11, 2016, https://www.opb.org/news/article/black-lives-matter-report-tweet-quoting-public-enemy-prompted-doj-investigation.
Ben Popper, “How the NYPD Is Using Social Media to Put Harlem Teens Behind Bars,” Verge, December 10, 2014, https://www.theverge.com/2014/12/10/7341077/nypd-harlem-crews-social-media-rikers-prison.
See Malachi Barrett, “How Authorities Use Social Media to Aid Investigations,” Government Technology, August 11, 2021, https://www.govtech.com/news/how-authorities-use-social-media-to-aid-investigations.
Kashmir Hill, “Eight Months Pregnant and Arrested After False Facial Recognition Match,” New York Times, August 6, 2023, https://www.nytimes.com/2023/08/06/business/facial-recognition-false-arrest.html; Katie Hawkinson, “In Every Reported Case Where Police Mistakenly Arrested Someone Using Facial Recognition, That Person Has Been Black,” Business Insider, August 6, 2023, https://www.businessinsider.com/in-every-reported-false-arrests-based-on-facial-recognition-that-person-has-been-black-2023–8; Khari Johnson, “Face Recognition Software Led to His Arrest. It Was Dead Wrong,” Wired, February 28, 2023, https://www.wired.com/story/face-recognition-software-led-to-his-arrest-it-was-dead-wrong; and Khari Johnson, “How Wrongful Arrests Based on AI Derailed 3 Men’s Lives,” Wired, March 7, 2022, https://www.wired.com/story/wrongful-arrests-ai-derailed-3-mens-lives.
Melissa De Witte, “Gang-Associated Youth Avoid Violence by Acting Tough Online, Stanford Sociologist Finds,” Stanford News Service, May 1, 2019, https://news.stanford.edu/press-releases/2019/05/01/gangs-use-social-media.
Forrest Stuart, Ballad of the Bullet: Gangs, Drill Music, and the Power of Online Infamy (Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 2020).
Nathan Bernard, “Maine Spy Agency Spread Far-Right Rumors of BLM Protest Violence,” Mainer, July 7, 2020, https://web.archive.org/web/20220218053843/https://mainernews.com/maine-spy-agency-spread-far-right-rumors-of-blm-protest-violence.[/fn] And online platforms can supercharge the reach of inaccurate information, as when a young South Asian student was wrongly identified as one of the Boston Marathon bombers, devastating his family. See Jay Caspian King, “Should Reddit Be Blamed for the Spreading of a Smear?,” New York Times, July 25, 2013, https://www.nytimes.com/2013/07/28/magazine/should-reddit-be-blamed-for-the-spreading-of-a-smear.html; and NPR, “How Social Media Smeared a Missing Student as a Terrorism Suspect,” April 18, 2016, https://www.npr.org/sections/codeswitch/2016/04/18/474671097/how-social-media-smeared-a-missing-student-as-a-terrorism-suspect.
Natasha Duarte, Emma Llansó, and Anna Loup, Mixed Messages? The Limits of Automated Social Media Content Analysis, Center for Democracy and Technology, November 2017, 3, https://cdt.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/Mixed-Messages-Paper.pdf.
Lizzie O’Leary, “Why Expensive Social Media Monitoring Has Failed to Protect Schools,” Slate, June 4, 2022, https://slate.com/technology/2022/06/social-media-monitoring-software-schools-safety.html.
Meta, “Meta Platform Terms,” updated April 25, 2023, https://developers.facebook.com/terms/dfc_platform_terms/#datause; and X Corp., “Developer Terms: More About Restricted Uses of the Twitter APIs,” accessed December 27, 2023, https://developer.twitter.com/en/developer-terms/more-on-restricted-use-cases.
Dirk Hovy, “Demographic Factors Improve Classification Performance,” Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 7th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing 1 (July 2015): 752–62, https://aclanthology.org/P15–1073.pdf.
See Gabriel Nicholas and Aliya Bhatia, Lost in Translation: Large Language Models in Non-English Content Analysis, Center for Democracy and Technology, May 2023, https://cdt.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/non-en-content-analysis-primer-051223–1203.pdf.
U.S. v. Jones, 565 U.S. 400, 416 (2012) (Sotomayor, J., concurring) (quoting U.S. v. Cuevas-Perez, 640 F.3d 272, 285 (7th Cir. 2011)) (internal quotation marks omitted).
Jonathan Vanian, “Meta Sues Voyager Labs, Saying It Created Fake Accounts to Scrape User Data,” CNBC, January 12, 2023, https://www.cnbc.com/2023/01/12/meta-sues-voyager-labs-over-scraping-user-data.html; and Rachel Levinson-Waldman and Gabriella Sanchez, “Meta Sues Surveillance Firm That Worked with Police,” Brennan Center for Justice, January 26, 2023, https://www.brennancenter.org/our-work/analysis-opinion/meta-sues-surveillance-firm-worked-police. According to an amended complaint filed by Meta, Voyager continued to create fake accounts and scrape data from hundreds of thousands of Facebook users even after Meta served the company with multiple cease-and-desist letters and filed suit.
Rachel Levinson-Waldman, “Directory of Police Department Social Media Policies,” Brennan Center for Justice, updated February 7, 2024, https://www.brennancenter.org/our-work/research-reports/directory-police-department-social-media-policies.
David Schuman, “NAACP Files Lawsuit Against Minneapolis for Alleged Discriminatory Social Media Surveillance,” WCCO (CBS News Minnesota), updated April 26, 2023, https://www.cbsnews.com/minnesota/news/naacp-files-lawsuit-against-minneapolis; and Minnesota Department of Human Rights v. City of Minneapolis, 27CV234177 (Minn. Dist. Ct. March 31, 2023), https://mn.gov/mdhr/assets/Court%20Enforceable%20Agreement_tcm1061–571942.pdf.
Jonah Kaplan, “MPD Settlement Agreement Approved, Altering the Future of Policing in Minneapolis,” WCCO (CBS News Minnesota), March 31, 2023, https://www.cbsnews.com/minnesota/news/minneapolis-state-officials-unanimously-approve-court-enforceable-settlement-agreement. Limitations for offline undercover operations have been an important part of consent decrees in places like New York City, where police have a long history of targeting political groups seeking racial justice. See Hamid Hassan Raza v. City of New York, No. 13CV3448 (E.D.N.Y. March 20, 2017), stipulation of settlement and order, exhibit A, 16–17, https://static1.squarespace.com/static/5c1bfc7eee175995a4ceb638/t/5d2f69ca7df2d700014089b8/1563388365355/Revised+Handschu+Guidelines.pdf.
Roy Austin, vice president of civil rights and deputy general counsel, Meta, letter to Michel Moore, chief, Los Angeles Police Department, November 11, 2021, https://about.fb.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/LAPD-Letter.pdf; Andrea Kirkpatrick, director and associate general counsel for security, Facebook, letter to Michael Rallings, director, Memphis Police Department, September 19, 2018, https://www.eff.org/document/facebook-letter-memphis-police-department-fake-accounts; and Levinson-Waldman and Sanchez, “Meta Sues Surveillance Firm That Worked with Police.” See also Mara Hvistendahl, “FBI Provides Chicago Police with Fake Online Identities for ‘Social Media Exploitation’ Team,” Intercept, May 20, 2022, https://theintercept.com/2022/05/20/chicago-police-fbi-social-media-surveillance-fake.
Social media is here to stay, and no configuration of legal and policy safeguards will eliminate the possibility of harm or misuse. Circumstances will arise in which investigating a crime or ensuring public safety necessitates using social media to view or gather information. At a minimum, police agencies should have a legitimate law enforcement purpose to monitor or collect social media data, although that requirement alone would still risk permitting far too much online information gathering with too few guardrails.
Accordingly, and given the harms articulated above, local, regional, and state law enforcement agencies that use social media for investigative and other purposes should develop and implement policies and practices consistent with the recommendations outlined below. These policies should include substantial mechanisms for input from community members and experts in privacy, civil rights, and civil liberties, among other fields. Best practices will evolve as more information emerges about both the benefits and risks of this technology. Policies would also benefit from legislation making them legally enforceable through private lawsuits.
Agencies that use social media monitoring in furtherance of their official missions should have publicly available policies that describe their practices and set out restrictions and oversight requirements. Those policies should contain the following provisions:
1. Criminal Investigations
Social media data may be viewed, monitored, or collected only when an agency has established specific and articulable facts showing reasonable grounds to believe that the data is relevant and material to an ongoing criminal investigation. Information gathered from social media should be documented in cases’ investigative files as soon as is practicable.
Data collected should not be shared with other law enforcement agencies absent either a showing of reasonable suspicion that the information contains evidence of criminal activity over which the receiving agency has jurisdiction, or relevance to an ongoing investigation or pending criminal trial in which the receiving agency is then engaged. Agencies should also have a memorandum of agreement in place confirming that the receiving agency will abide by equivalent limitations in any use or further dissemination of the data.
When agency use of social media is likely to yield information about First Amendment–protected rights, best practices regarding profiling and targeting of constitutionally protected activity (discussed below) should be followed.
2. Preparation for Public Events
Publicly available social media content may be monitored or viewed in advance of significant public events solely to determine the resources necessary to keep participants and the public safe. When agencies can make these determinations in ways that do not risk incidentally viewing First Amendment–protected information — such as by consulting a permit application or contacting an event organizer directly — these means are preferred. All social media monitoring should be approved by an individual at the rank of police chief or a named senior-level designee.
Social media surveillance should only be undertaken when specific, articulable, and credible facts demonstrate a public safety concern justifying the monitoring. Such concerns and the supporting facts should be documented in writing. The documentation should include a description of the social media searches to be made, including identification of any search terms, individuals, or hashtags monitored; the justification(s) for those searches; and the factor(s) necessitating social media as a necessary tool for making resource determinations.
A determination that a public safety concern exists should never be based to any degree on the constitutionally protected political or religious beliefs or the ethnic, racial, national, or religious identity of an individual or group, nor should it be based on violence at a previous event that resulted from police activity.
Only data relevant to a law enforcement agency’s resource and planning determinations to ensure public safety should be collected. If officers find no indication of criminal activity while monitoring, then social media data should not be retained past the event date. If online surveillance uncovers information connected to an existing criminal investigation, then that data may be retained in accordance with relevant statutes and departmental rules. footnote1_cV48GT2vPeJs 1 Global Advisory Committee, Recommendations for First Amendment–Protected Events for State and Local Law Enforcement Agencies, Office of Justice Programs, Department of Justice, December 2011, 12, https://bja.ojp.gov/sites/g/files/xyckuh186/files/media/document/Role_of_State_and_Local_Law_Enforcement_at_First_Amendment_Events_Reference_Card.pdf.
Data should not be shared with other law enforcement agencies absent a demonstrable showing of necessity to address a specific and articulated public safety concern and a memorandum of agreement with the receiving agency confirming that it will abide by the limitations set out above in any use or further dissemination of the data.
3. Evaluation of Social Media Information
Any information collected from social media must be evaluated for validity and reliability prior to being used as criminal intelligence and must be authenticated before being used in a criminal investigation. footnote2_ypNNAFSD8rgG 2 See Global Advisory Committee, Developing a Policy on the Use of Social Media, 15–16.
4. Controls for Undercover Account Use
Because of the risk of abuse and the inherent lack of transparency, as well as platform policies prohibiting their use, undercover accounts should be used extremely sparingly if at all, and only with a policy in place that requires:
Permission to impersonate an actual person in the course of an approved criminal investigation should be limited to a narrow set of circumstances (e.g., assisting in identifying an online stalker) — the officer must, in addition to satisfying the restrictions above, obtain the permission of the person being impersonated, Officers may not change the individual’s password or alter other private or sensitive information related to the account without explicit consent, and may not take any actions — including interacting with individuals or groups or posting on behalf of the impersonated individual — beyond the pre-determined limited set of actions necessary to carry out the investigation. Furthermore, the impersonated person must be allowed to withdraw permission at any point, at which time the officer must immediately cease use of and access to the account. All undercover activity on the impersonated account must be properly documented in the investigative file.
5. Protections Against Profiling and Targeting of Constitutionally Protected Activity
Collection or monitoring of social media is prohibited when it is based to any degree on the race, religion, ethnic or national origin, gender or gender identity, sexual orientation or characteristics, or immigration status of an individual or group, except when trustworthy information specific and limited in time and location links persons possessing these traits to the description of individuals suspected of criminal activity, or it is based to any degree on a person’s exercise of First Amendment freedoms, or is reasonably likely to chill the exercise of such freedoms, except where there is reasonable suspicion of criminal activity or planning and clear evidence indicates that the First Amendment–protected activity directly relates to the suspected criminal activity or planning, or in the narrow context of event planning (subject to the restrictions set forth above).
When social media use during a criminal investigation is reasonably likely to yield information about the exercise of First Amendment–protected rights, data collection should not commence until the following measures have been met:
6. Whistleblower Protections
Protections to prevent retaliation against internal whistleblowers who disclose violations or abuses of social media monitoring practices — along with effective redress mechanisms — must be in place.
7. Contracting Limitations
The police department or its contracting authority must require any vendor to agree to be bound by any of the above conditions that are relevant to the vendor’s services. They should also obtain from vendors a demonstration or other explanation of how they will comply. Law enforcement agencies may not contract with any vendor who cannot or will not adhere to these requirements.
Every law enforcement agency that uses social media monitoring for investigative, intelligence, or event-planning purposes should publish a regular written report at least every two years. These reports should include the following information at a minimum:
Jurisdictions should hold public hearings and obtain local government oversight and approval before contracting with vendors that facilitate the collection or analysis of social media data for the permitted purposes described above. The oversight and approval process must include considerations of cost, effects (including potential repercussions for marginalized communities and First Amendment–protected activities). The process should also outline accountability and oversight measures, and it should require a demonstration of efficacy evaluated and validated by an independent third party. Any contract must include stringent oversight, auditing, and public disclosure measures.
Independent oversight entities should audit every law enforcement agency’s social media monitoring practices and disclosures on an ongoing basis to ensure compliance with departmental policies and with constitutional protections and safeguards. The results of each audit should be posted publicly on the agency’s website.
Global Advisory Committee, Recommendations for First Amendment–Protected Events for State and Local Law Enforcement Agencies, Office of Justice Programs, Department of Justice, December 2011, 12, https://bja.ojp.gov/sites/g/files/xyckuh186/files/media/document/Role_of_State_and_Local_Law_Enforcement_at_First_Amendment_Events_Reference_Card.pdf.
See ACLU of Tennessee v. City of Memphis, No. 17CV02120 (W.D. Tenn. September 21, 2020), amended judgment and decree (“Modified Kendrick Decree”), 9, https://www.memphispdmonitor.com/_files/ugd/03602e_a3fae3908fa74b2aa1e325ce181de427.pdf.%5b.
While many departments have policies addressing the use of social media data, most are too permissive or provide little transparency about actual practices.
August 29, 2024
Hundreds of law enforcement agencies lack the safeguards needed to prevent officers from misusing social media to target First Amendment activity and minorities. Our best practices show how to fill the gaps.
February 7, 2024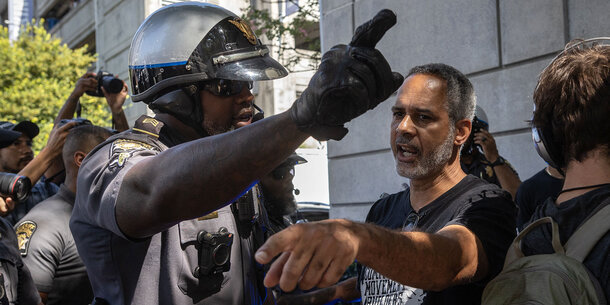
The documents show inappropriate police surveillance of social media posts about pizza nights and study groups.